How to Fix Page Indexing Issues on Your Website
- by Ilona K.

Table of contents
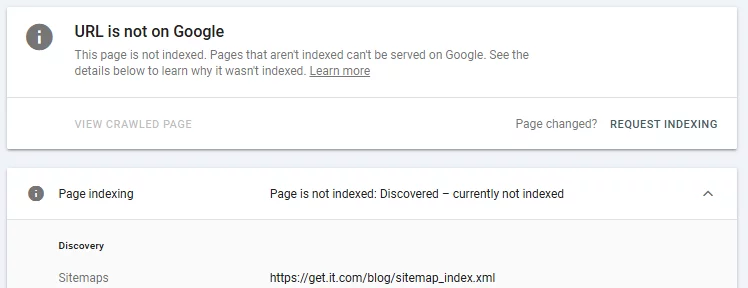
Every owner of a growing site wants to see new pages appear in Google within days, not months. Yet Search Console can throw back warnings like “Discovered - currently not indexed,” leaving traffic-hungry pages stuck in limbo.
This guide explains what a page indexing issue is, why it happens, and the practical steps many businesses use to nudge their content into the Google index. By the end, you’ll know how to spot problems early and choose the right fixes for your site.
What Page Indexing Means and Why It Matters
Indexing is Google’s way of filing each crawled page in its vast library. When a URL sits outside the index, it cannot show up in search results, so potential customers never reach it. With Google indexing fewer new URLs since May 2025 – earning a spot has only become tougher.
Dan Taylor, a prominent SEO expert, shared the insights from the most recent Google Search Central Live showing most common indexing signals - such as country, language, HTTPS, Core Web Vitals, DoFollow links, content freshness and compliance.

Crawling vs indexing
- Crawling is Googlebot’s (a web crawler used by Google to discover, crawl, and index web pages) visit to fetch a URL. If Google crawled your website’s page, it does not guarantee it will appear in search results.
- Indexing is the decision to keep that page in search results. It means the page and its content has been added to Google’s library.
A page marked Crawled – currently not indexed passed the first gate but stalled at the second. The “Discovered” variant means Googlebot has your URL in its queue yet hasn’t crawled it at all.
Why “Discovered - Currently not Indexed” Appears
Website owners frequently ask why are your pages discovered, but not indexed – a hint that the problem is common. Google budgets a limited number of requests to each site - often referred to as crawl budget. If that crawl budget is tight – due to duplicate pages, redirect chains, or slow responses – new URLs may wait in line.
Common Reasons Pages Skip the Google Index
Some common Google indexing issues include:
- Large numbers of near-duplicate pages.
- Thin or boilerplate content - think less than 100 words on a page.
- No internal links from other website pages or the main menu pointing to the page.
- Misconfigured robots.txt (a simple text file placed at your site’s root that tells search-engine crawlers which pages they may or may not visit) or noindex tags (an HTML meta directive that instructs search engines not to add the page to their index).
- Server errors or timeouts during crawl.
In May 2025 Google confirmed it is “being more selective” with low-value pages, reinforcing the need for clear signals of quality.
Step-by-Step Checklist to Fix Page Indexing Issues
Fixing page indexation issues can be tedious - however, the six steps below help resolve the most common problems.
1. Verify Status in the Page Indexing Report
Open Search Console and inspect the affected URL, then view the page indexing report for site-wide patterns. The report labels each URL with reasons such as Duplicate, submitted URL not selected or Alternate page with canonical tag. Knowing the exact label guides the next action.
2. Maintain a Clean Sitemap
A well-formed sitemap is the fastest way to teach Google which URLs matter. Submit it in Search Console and update it whenever you add or remove pages.
3. Optimize Crawl Budget
Reduce dead-end paths so Googlebot spends less time on junk and more on revenue-generating or otherwise priority pages:
- Remove soft-404 pages and looping redirects.
- Consolidate near-duplicates with canonical tags.
- Serve stable, fast responses (aim for <500 ms time to first byte).
Balancing crawl budget often goes hand in hand with efforts to fix traffic drops.
4. Strengthen On-Page Signals
Pages with rich, original information and clear structure are more likely to earn a crawl invite and stick in the index:
- Add descriptive headings and internal links.
- Use structured data where it supports the topic.
- Check that meta titles align with search intent.
- Ensure your website copy is rich, informative, original and follows Google’s best practices.
Need a refresher? See our guide on optimize information displayed in Google.
5. Fix Technical Roadblocks
Security warnings, mixed protocols, and expired SSL certificates can discourage bots. If Search Console flags Security issues, our walkthrough on how to fix “your connection to this site is not secure” outlines the usual remedies.
Server logs can also reveal spikes in 5xx errors that squander crawl budget. An owner of bakery.it.com trimmed daily errors from 150 to under 5, and Google indexed a new menu page within 48 hours.
6. Request Reindexing and Monitor
After significant fixes, many site owners request a fresh crawl via the URL Inspection tool. While this action doesn’t guarantee indexing, it often accelerates the review. Pair it with GA4 checks – our primer on how to fix “unassigned” traffic helps keep analytics data clean for monitoring impact.
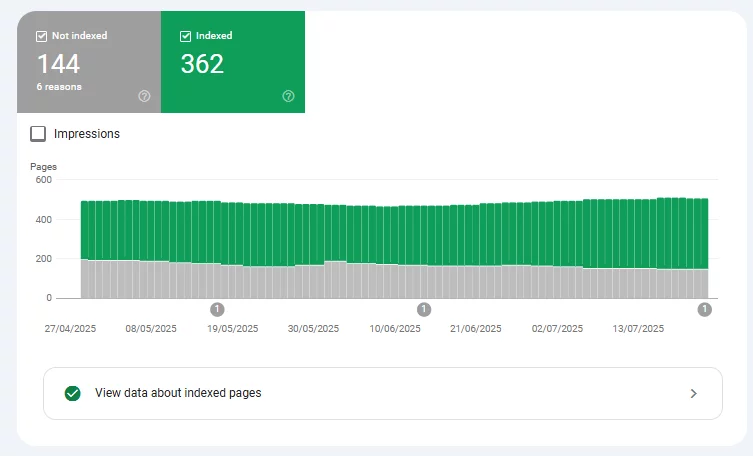
Measuring Success

Track impressions for target pages in Search Console and keep an eye on the Valid trend line in the Page Indexing report. A steady rise in indexed URLs and stable performance metrics suggests your changes are paying off.
A thoughtful approach to crawl budget, content quality, and technical hygiene can turn “Discovered - currently not indexed” into a distant memory. By keeping sitemaps current, tightening on-page signals, and watching Search Console alerts, businesses often see faster website indexation and smoother growth.
FAQs
What do page indexing issues mean?
They signal that Google has either not crawled a URL or decided not to store it in its index, so the page cannot appear in search results.
What is the indexing problem?
An indexing problem is any condition – technical, content-related, or policy-related – that causes Google to skip adding a page to its searchable database.
How to fix indexing problems?
Site owners typically check Search Console’s Page Indexing report, address the listed reasons (such as duplicate content or server errors), and then request reindexing.
Why are my pages not indexing?
Common causes include thin or duplicate content, blocked resources in robots.txt, slow server responses, and limited crawl budget.
How to check if a page is indexed or not?
In Google Search Console, paste the URL into the URL Inspection bar; it will show the URL is on Google if the page is indexed or explain why it is not.
Achieve success online faster - visit it.com Domains blog and follow us on social media.

Read also

Tips and Tricks
AI Appreciation Day: Top-10 Domain Names for AI Startups on it.com Domains
- 3 min read

